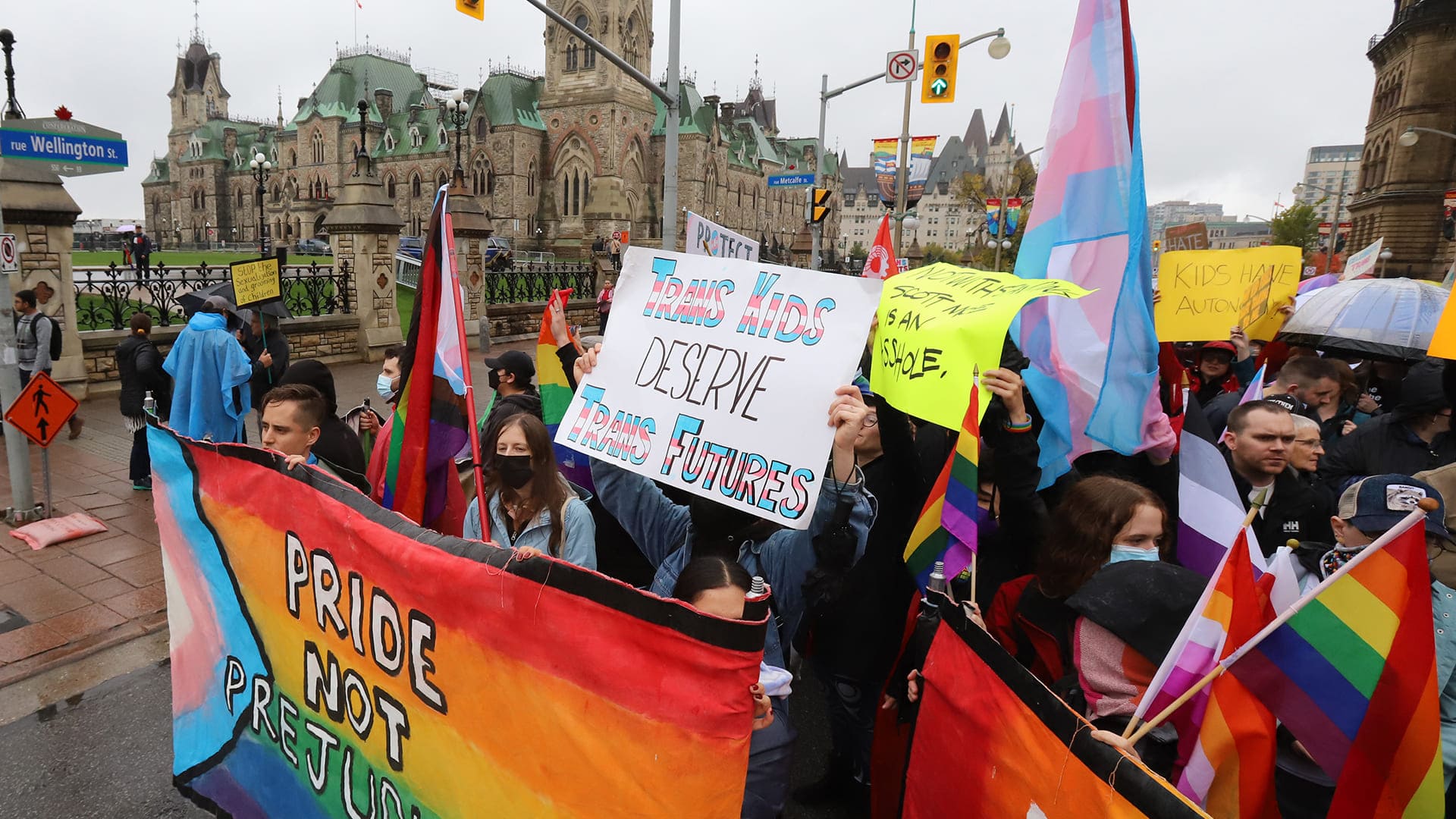
Since the legalization of same-sex partnerships in 2005 and the 1969 banning of homosexuality, Canada has made great strides toward the advancement of LGBTQ+ rights. But problems like acceptance and rights for transgender people still exist. This article looks at these issues and emphasizes Canada's continuous initiatives to build a more just and inclusive country. The absence of extensive legal safeguards is one issue facing transgender people. Although several provinces have passed laws, uniform national legislation is still required to guarantee equal rights for all transgender individuals. Different locations have different levels of societal acceptance and understanding of LGBTQ+ people, which highlights the necessity for constant education and awareness.
I. The Evolution of LGBTQ+ Rights
Since the decriminalization of homosexuality in 1969 and the legalization of same-sex partnerships in 2005, Canada has made tremendous progress toward the advancement of LGBTQ+ rights. A more inclusive legal system and federal law prohibiting discrimination based on gender identity are the results of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, which guarantees fundamental freedoms free from discrimination based on sexual orientation. The establishment of LGBTQ+ community centers and groups offers vital information and assistance, promoting a feeling of acceptance and secure environments for people who identify as LGBTQ+. The Canadian government has put laws into place that support the inclusion of LGBTQ+ people in healthcare and education.
II. Laws Prohibiting Discrimination
Anti-discrimination legislation have been put in place in Canada to safeguard LGBTQ+ people in the workplace, in housing, and in social services. Nonetheless, there are obstacles to enforcement, especially in the employment and service sectors. One problem that contributes to prejudice is employers' and service providers' ignorance. For successful regulation and deterrence, stronger sanctions and repercussions for violators are required. Education and advocacy groups can raise awareness and work with lawmakers to push new legislation and reinforce existing ones, thereby increasing legal safeguards.
III. Transgender Rights and Legal Recognition
Despite progress in LGBTQ+ rights, the transgender community still faces unique challenges due to varying laws across provinces and territories. Proponents of uniform national legislation are pushing for uniform protection of transgender rights, as without these laws, they may struggle to access basic services like housing, work, and healthcare, and may face further marginalization due to unclear and discriminatory practices.
IV. Conversion Therapy Bans
The goal of the Canadian LGBTQ+ rights movement is to outlaw conversion therapy, a contentious practice that involves using religious rites or psychotherapy to change a person's gender or sexual orientation. Medical and psychiatric groups have denounced this technique for its detrimental consequences on LGBTQ+ people as well as its ineffectiveness. Several nations have already outlawed conversion therapy, understanding how crucial it is to safeguard human rights and general welfare. Conversion therapy is now illegal in a number of territories and provinces, underscoring the rising significance of defending the rights and welfare of the LGBTQ+ population.
A nationwide ban on conversion treatment is lacking, which raises questions regarding the efficacy of certain provincial laws. Proponents contend that a federal prohibition would offer uniform protection for LGBTQ+ people across Canada and convey a clear message that sexual orientation therapy is undesirable, supporting a coordinated, national strategy to abolish this damaging practice. Additionally, this strategy would stop people from looking for hazardous activities in places where they are still permitted.
V. Challenges in Education and Awareness
Legal safeguards are important, but there are still obstacles in the way of encouraging LGBTQ+ inclusiveness in educational environments. The persistence of bullying and discrimination in schools due to sexual orientation and gender identity highlights the necessity of comprehensive education and awareness initiatives. The goal of incorporating LGBTQ+ history into school curricula is to close the gap; nevertheless, continuous lobbying is necessary to advance inclusiveness and dispel negative stereotypes. In addition to tools and support networks that can assist LGBTQ+ kids overcome obstacles and develop a sense of belonging within the school community, training for educators and staff is essential to establishing a safe environment for these students.
VI. Intersectionality and Inclusivity
Complicating the battle for inclusiveness is the interconnectedness of LGBTQ+ identities with other facets of an individual's identity, such as race, ethnicity, and disability. The issues encountered by persons who are at the junction of many marginalized identities are unique, and legal frameworks must adapt to meet their needs.
Conclusion
Notwithstanding, obstacles endure, and the continuous development of legal structures is imperative to tackle new concerns. Canada can maintain its leadership in promoting LGBTQ+ rights by raising awareness, implementing anti-discrimination laws, and resolving legal recognition gaps. The legal environment is constantly evolving, necessitating ongoing efforts to uphold equality, respect, and dignity. Positive developments include legalizing same-sex unions and protecting gender identity in human rights laws. However, more work is needed to address issues like housing and employment discrimination, transgender healthcare access, and conversion therapy. Canada's legislative structures must be updated to reflect the changing requirements of the society while maintaining its vigilance.




